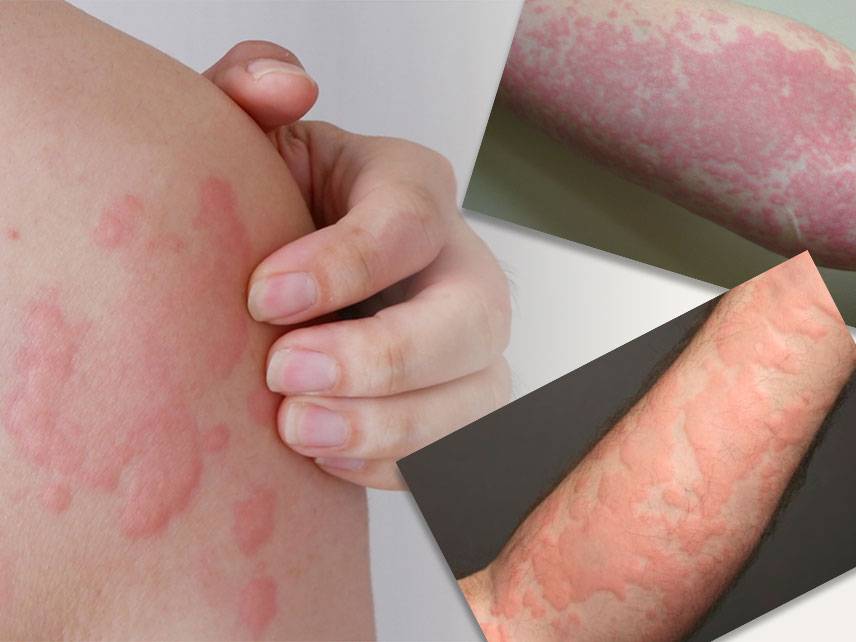
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin disorder characterized by raised, itchy, red welts. Although it is usually not serious, it can be a very uncomfortable condition for those affected. In some cases, the symptoms can be severe and even life-threatening. This article will explore the signs, causes, and risk factors of urticaria, as well as the treatment and prevention of the condition.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of urticaria is itchy, raised welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape. These welts can be red, skin-colored, or pale, and they may be accompanied by a burning sensation. In some cases, the welts may blister or swell and become warm to the touch. Other symptoms may include swelling in the face or throat, difficulty breathing, and hives that occur in the same area of the body for more than six weeks.
Causes
The exact cause of urticaria is often unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an allergic reaction or contact with an irritant. In some cases, urticaria can be caused by an infection or an underlying medical condition such as an autoimmune disease. Certain medications and foods can also trigger an attack of hives.
Risk Factors
Anyone can develop urticaria, but people with a history of allergies or a weakened immune system are at an increased risk of developing the condition. Other risk factors include exposure to cold or heat, stress, and certain medications.
Prevention
The best way to prevent an attack of urticaria is to identify and avoid any triggers that you may have. This includes avoiding foods, medications, and environmental irritants that may cause an allergic reaction. Additionally, it is important to manage stress and get adequate rest to reduce the risk of an attack.
Diagnosis
If you experience symptoms of urticaria, it is important to see a doctor. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and may conduct an allergy test or skin biopsy to confirm a diagnosis. They may also run tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be causing the hives.
Treatment
Treatment for urticaria will depend on the severity of the symptoms. Mild cases may be treated with antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling. In more severe cases, corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed.
Coping and Support
Living with urticaria can be difficult and it is important to find ways to cope with the condition. It can help to join a support group, where you can discuss your experiences with others who have similar conditions. Additionally, it is important to practice self-care and to make lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of an attack.
Complications
In some cases, urticaria can lead to more serious complications such as anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, or swelling of the face or throat.
Living with Urticaria
Living with urticaria can be a challenge, but there are ways to manage the condition. It is important to identify and avoid triggers, take medications as prescribed, and practice stress management and self-care. With the right treatment, it is possible to control the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Urticaria is a skin disorder that can be uncomfortable and even life-threatening in some cases. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms, identify triggers, and seek medical treatment if needed. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications.